What is a terminating decimal?
A terminating decimal is a decimal number that has digits that eventually end. In other words, it doesn't go on forever.
Examples:
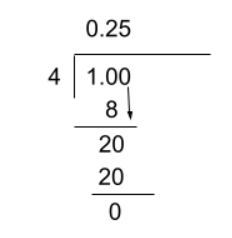
- 0.15 is a terminating decimal because it does not go on forever. It stops after two decimal places
- 0.2345 is a terminating decimal because it does not go on forever. It stops after four decimal places.
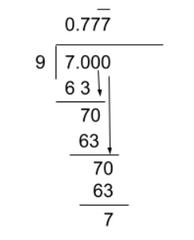
In contrast, there are decimals that go on forever, or are recurring decimals. These numbers have digits that will go on forever.
Examples:
- 0.33333… is a recurring decimal because it continues to repeat 3 forever.
A good way to think about terminating decimals is to think about the definition of terminate. When something is terminated or terminates, it ends.
How can we use the concept:
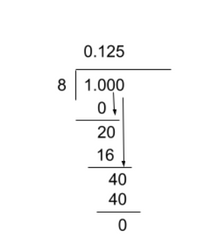
To solve for a terminating decimal, one must know how to convert a fraction to a decimal. To do this, follow the following steps:
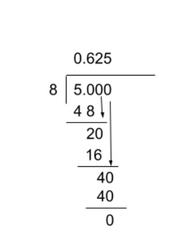
5/8 (See below for the solution)
- Read the fraction from top to bottom like so: “five divided by 8.” This will indicate to you that the numerator needs to go in the house (the dividend) and the denominator will go on the outside (the divisor).
- Divide normally if possible. If it is not, add a decimal and a zero after. This does not change the value of the number, but allows you to have more place values to work with.
- Stop when there is nothing left (no remainders/the decimal terminates) or where the question asks you to round to.